Eg the T4 nerve root runs between the T4 vertebra and T5 vertebra. Internal branch of the posterior divisions of the upper six thoracic nerves run between the Semispinalis dorsi and Multifidus which they supply.

Illustration Of Variation Of Position Of Medial Branch In Thoracic Download Scientific Diagram
Each vertebral segment has two facet joints one on each side.

. Thoracic spinal pain can be as chronic and disabling as neck and low back pain even though it is less common. See Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots. The medial branch nerve was also ablated at L4 L5 and the dorsal ramus at the sacral ala with the same results and without complications on the left.
The internal thoracic artery internal mammary artery is a long paired vessel that originates from the proximal part of the subclavian artery. The medial branch then runs around the lateral border of the superior articular process and enters the fibro-osseous canal. The thoracic spine has.
A mixed nerve containing both motor and sensory fibers. Sympathetic innervation to the skin. The cervical facet joints guide motion in the neck and the thoracic facet joints guide motion in the mid-back.
Cervical or Thoracic Medial Branch Block Facet Nerve Injections The facets are the small bony joints that connect one spine vertebra to another at the back of the spinal canal. 12 nerve roots T1 to T12 on each side of the spine that branch from the spinal cord. Thoracic medial branch nerves are located over a bone in the mid-back or upper back.
Prior to the steroid injection you will be lying on your stomach. They transmit pain signals from the facet joints to your brain. The site of the.
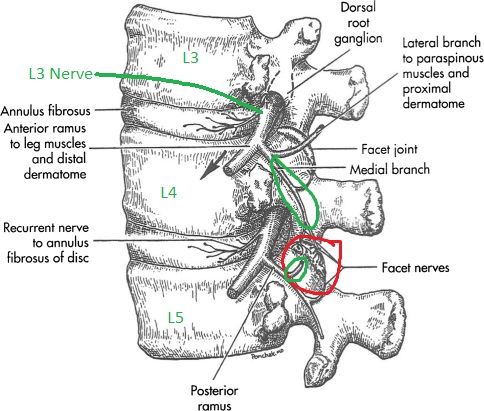
The posterior ramus of the thoracic nerve passed through the narrow space between the bony structures and adjacent fibrous tissue. Each thoracic spinal nerve is named for the vertebra above it. Anatomy Each facet joint is innervated by the medial branches of the posterior primary division of the spinal nerves above and below the joint Figure 4714.
Thoracic facet joints are named for the vertebrae they connect and the side of the spine where they are found. Duration Less than 15 minutes How is it performed. The medial nerves are uniquely located in each segment of the spine.
Cervical medial branch nerves are located in a bony groove in the neck. Non-pulsed radiofrequency ablation was then performed at a temperature of 80 degrees Celsius at the probe tip for a duration of sixty seconds. The subclavian artery is divided into three parts based on its anatomical relationship to the anterior scalene muscle.
The needle tip is placed at the superior lateral edge of the transverse process where each. Medial branch nerves are found near facet joints. They give off two segmental arteries in each space.
To establish the anatomical basis for thoracic medial branch neurotomy an anatomical study was undertaken. A thoracic medial branch block is a diagnostic treatment intended to determine whether a particular thoracic facet joint is the source of your pain. The posterior cutaneous branches medial cutaneous branches of the posterior divisions of the thoracic nerves descend for some distance close to the spinous processes before reaching the skin while the lateral branches travel downward for a considerable distanceit may be as much as the breadth of four ribsbefore they become superficial.
General sense touch pressure pain heat cold etc to the skin of the back. These injections are performed with the use of a posterior approach. It runs inferomedially and enters the thoracic cage deep to the clavicle and the first rib.
The medial branches of the lower six are distributed chiefly to the. Total fluoroscopy time was minutes mGy. Using an X40 dissecting microscope a total of 84 medial branches from 7 sides of 4 embalmed human adult cadavers were studied.
It is sent to the first branch which is. First branch off of the ventral side of the spinal nerve. The medial branch runs in the groove formed by the lower transverse process and the superior articular process and then descends caudally and posteriorly accompanying the vessels arising from the lumbar artery and vein.
It descends on the deep surface of the rectus abdominis muscle within the rectus sheath and anastomoses with the inferior epigastric artery. Thoracic medial branch nerve injections are indicated for the diagnosis of axial thoracic ie mid back pain that typically originates from zygapophysial ie facet joint sprains contusions or osteoarthritis. To establish the anatomical basis for thoracic medial branch neurotomy an anatomical study was undertaken.
Branches of the internal thoracic artery superiorly and of the musculophrenic arteries inferiorly. Interventional Procedures We Offer Thoracic Medial Branch Blocks and Cooled RF Coolief The role of thoracic facet joints in chronic back pain has received very little attention as compared to lumbar and cervical facet joints. The medial branches of the thoracic dorsal rami were found to assume a reasonably constant course.
Each thoracic nerve root exits the spinal canal through an intervertebral foramen formed by two adjacent. Z-joint joint Multifidus Spinalis thoracis splenius cervicis rhomboids and trapezius upper levels only The medial branch follows a general path which displays certain level of variability between individuals and. The medial branches of the thoracic dorsal rami were found to assume a reasonably constant course.
First branch off of the dorsal side of the spinal nerve. The right T4-5 facet joint for example joins the 4th and 5th thoracic vertebrae on the right side. The medial branches ramus medialis.
Lumbosacral medial branch nerves are found in a bony groove in the low back. Using an X40 dissecting microscope a total of 84 medial branches from 7 sides of 4 embalmed human adult cadavers were studied. The cervical tho-racic or lumbar facet joints may be injected for diag-nostic and potentially therapeutic purposes.
One courses above in the costal groove and the other along the upper border of the rib below anastomosing with branches of the posterior arteries. The medial terminal branch of the internal thoracic artery. Thoracic medial branch nerve radiofrequency neurolysis is indicated for the treatment of axial thoracic ie mid back pain that typically originates from zygapophysial ie facet joint sprains contusions or osteoarthritis.
The left subclavian artery originates directly from the aortic arch and ascends in the mediastinum to the base of the neck where it follows on the left side a similar course to that of the right subclavian artery Fig. They then pierce the Rhomboidei and Trapezius and reach the skin by the sides of the spinous processes. The medial branch innervates.
To the deep back mm. Thus every joint is supplied by two or more adjacent spi-nal nerves. Detailed anatomy of the posterior ramus and mediallateral branches and their fine branches in the entire thoracic region was investigated by both macroscopic and stereomicroscopic dissections.
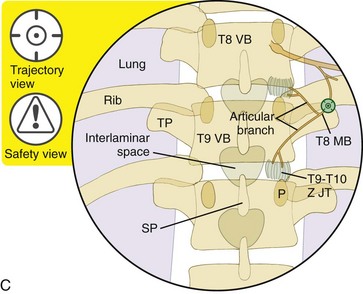
Thoracic Zygapophysial Joint Nerve Medial Branch Injection Posterior Approach Radiology Key

Illustration Of Variation Of Position Of Medial Branch In Thoracic Download Scientific Diagram
Fluoroscopic Guided Thoracic Medial Branch Block Technique And Overview The Procedure Guide

Illustration Of Medial Branch Mb And Lateral Branch Lb Thoracic Download Scientific Diagram
Thoracic Zygapophysial Joint Nerve Medial Branch Injection Posterior Approach Radiology Key
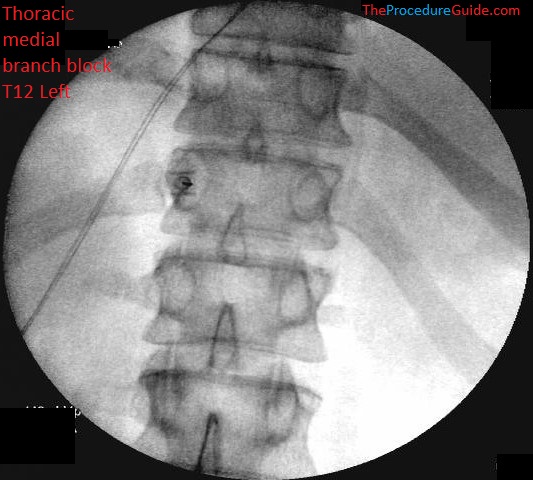
Fluoroscopic Guided Thoracic Medial Branch Block Technique And Overview The Procedure Guide

Thoracic Medial Branch Block Highland In Kanuru Interventional Spine And Pain Institute

0 comments
Post a Comment